Old technology – new applications: The torque converter transmission is still “in” and is very important in automotive engineering. It is used more frequently in hybrid engines, for example. But how does the technology work and what are the advantages and disadvantages?
Author
Oliver Hagenlocher
When the conversation turns to the topic of sustainability, most would assume green manufacturing and environmental protection will be the focus of the discussion. It’s part of the chat, Michael Tamasi, President and CEO of AccuRounds, argues, but to him and his company the term means much, much more. Yes, they’ve added solar panels to lower the plant’s carbon footprint; however, Michael knew building a company that will last involves attracting, developing and keeping talented staff. Retaining good employees also requires nurturing a creative and caring culture, and of course, operating a profitable business that provides long-term financial security as well as a good wage.
MR Components, a medium-sized company from Grigno, Italy, has significantly increased its production capacity and simultaneously improved quality by introducing intelligent automation with EMAG machines. The company, which specializes in the production of parts for differential and planetary gears, now produces around 80,000 components per month, with some of the machines running unmanned in the evenings. In conversation with Alessandro Reguzzo, owner and Managing Director of MR Components, we were able to find out more about the company’s production philosophy and design and development.
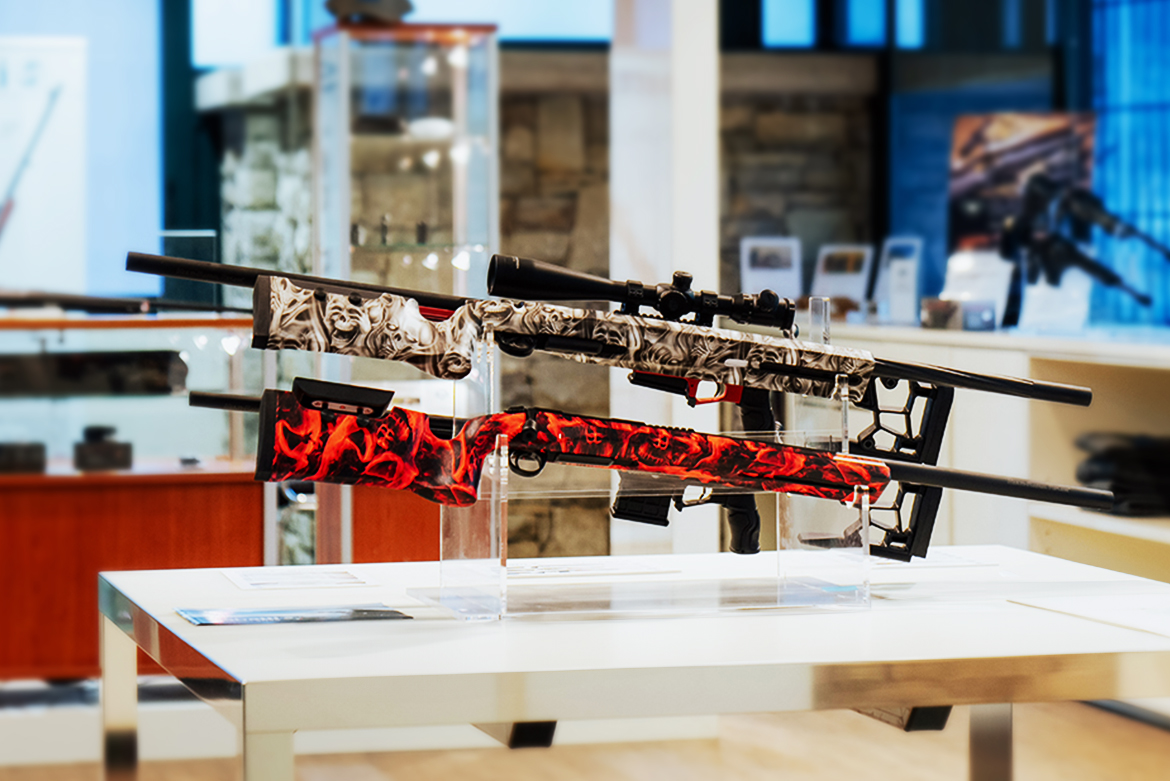
Sabatti Spa is a renowned family business whose origins go back 350 years with the gunsmith Ludovico Sabatti, is deeply rooted in the tradition of gunmaking. The actual company was founded in the post-war period by Antonio Sabatti and has since built a reputation for precision and craftsmanship. Under the direction of Emanuele Sabatti, the grandson of the company founder, Sabatti Spa has expanded its product range from simple gun parts to high-quality over-and-under shotguns, double-barrel shotguns and carbines. Manuel Steinhauer had the opportunity to interview Emanuele Sabatti, a visionary and technology enthusiast, who has led the company into the modern world of firearms technology without losing sight of its rich tradition and centuries-old heritage. Today, Sabatti Spa is at the forefront of innovation in firearms manufacturing, balancing time-honored craftsmanship with modern technology, making the company one of the leading names in the industry.
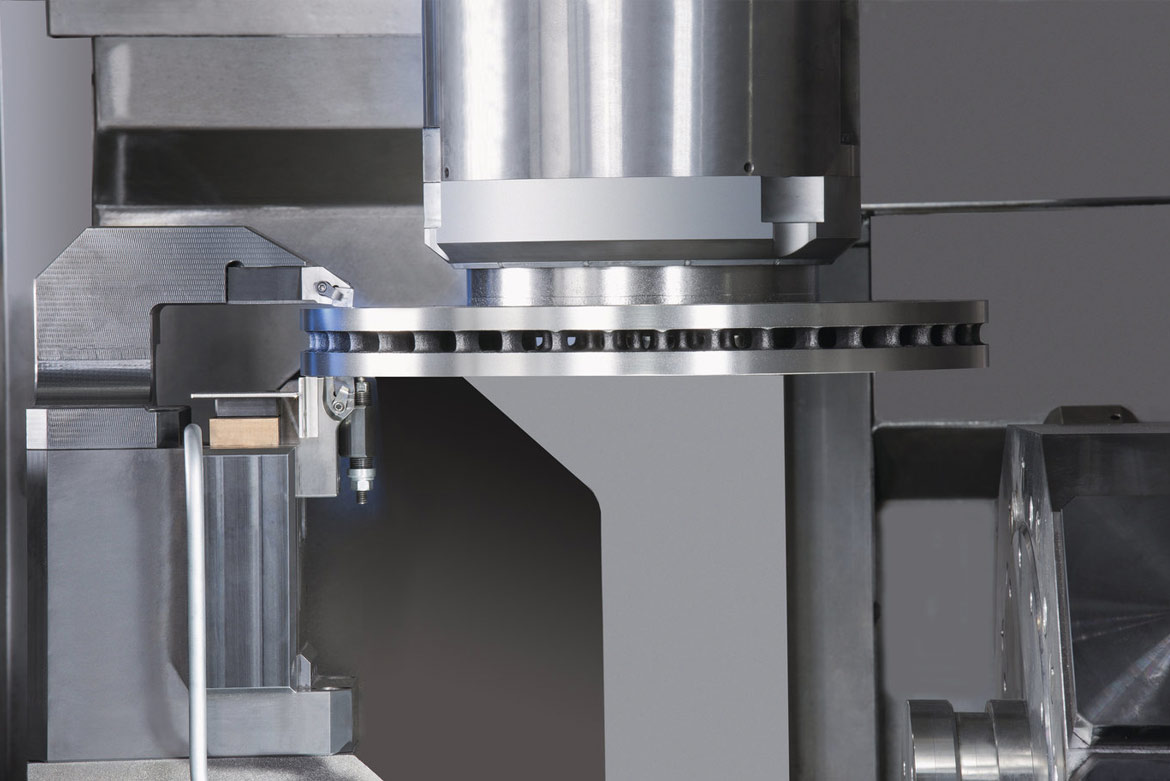
The brake disc is one of the most important safety-relevant components in passenger and commercial vehicles. The production of brake discs is, therefore, a demanding field of application that requires the highest precision. At the same time, cost pressures are very high and changing production batches must pass through the production lines with high productivity and short set-up times. As a specialist in the machining of brake discs, EMAG has already implemented numerous customized turnkey solutions in close cooperation with customers operating worldwide. In the following interview with Dominic Grimminger, expert for brake disc production systems at EMAG, we learn more about the challenges and solutions in this field of application.
In our latest interview, we take an in-depth look at the W 11 CNC cylindrical grinding machine from EMAG Weiss, a state-of-the-art solution designed specifically to meet the demanding requirements of today’s manufacturing industry. Known for its exceptional flexibility and precision, the machine maximizes the efficiency and accuracy of machining processes. With functions ranging from quick and easy retooling to intuitive dialog programming, the W 11 CNC sets new standards in the world of cylindrical grinding. Andreas Hessling, Technical Sales Manager at EMAG, gives an insight into the technical advantages and range of applications of the machine.
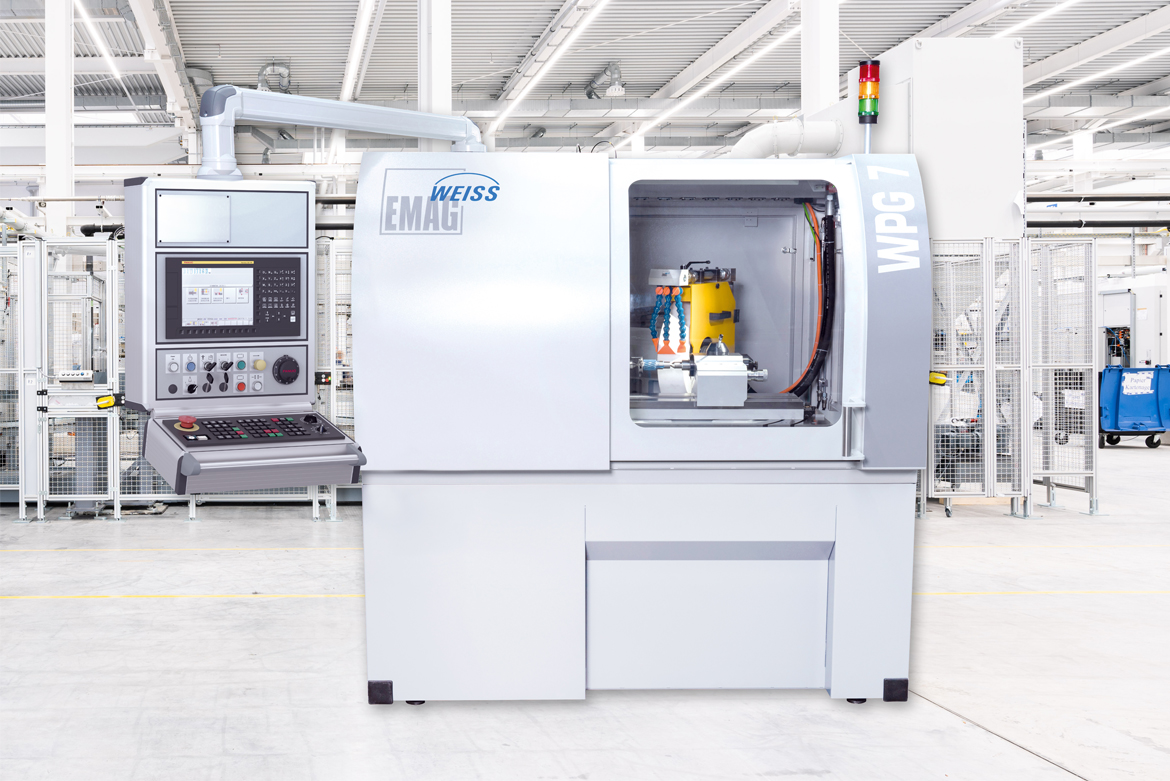
Precise, compact and cost-effective – these are the criteria that have made the WPG 7 external cylindrical grinding machine from EMAG WEISS a great success on the market. It requires minimal floor space and can also be installed quickly, but at the same time features a whole range of high-tech components for flexibility and productivity. What characterizes the machine in detail? Our grinding expert Andreas Holstein provides the answers in this interview.
The gear skiving process, also known as power skiving, is becoming increasingly popular with many users in the manufacture of gear components. This is no coincidence: compared to the shaping process, it is significantly faster and also offers more flexibility than hobbing and broaching. However, for a long time it was considered relatively complex. In this context, the VSC 400 PS represents a turning point – the application of power skiving is significantly simplified, as only minimal data is required from the operator, eliminating the need for extensive expertise in gear cutting. To take a closer look at the technology behind the VSC 400 PS and its impact on the industry, we interviewed Daniel Nille, Head of Technology Development for EMAG Power Skiving.