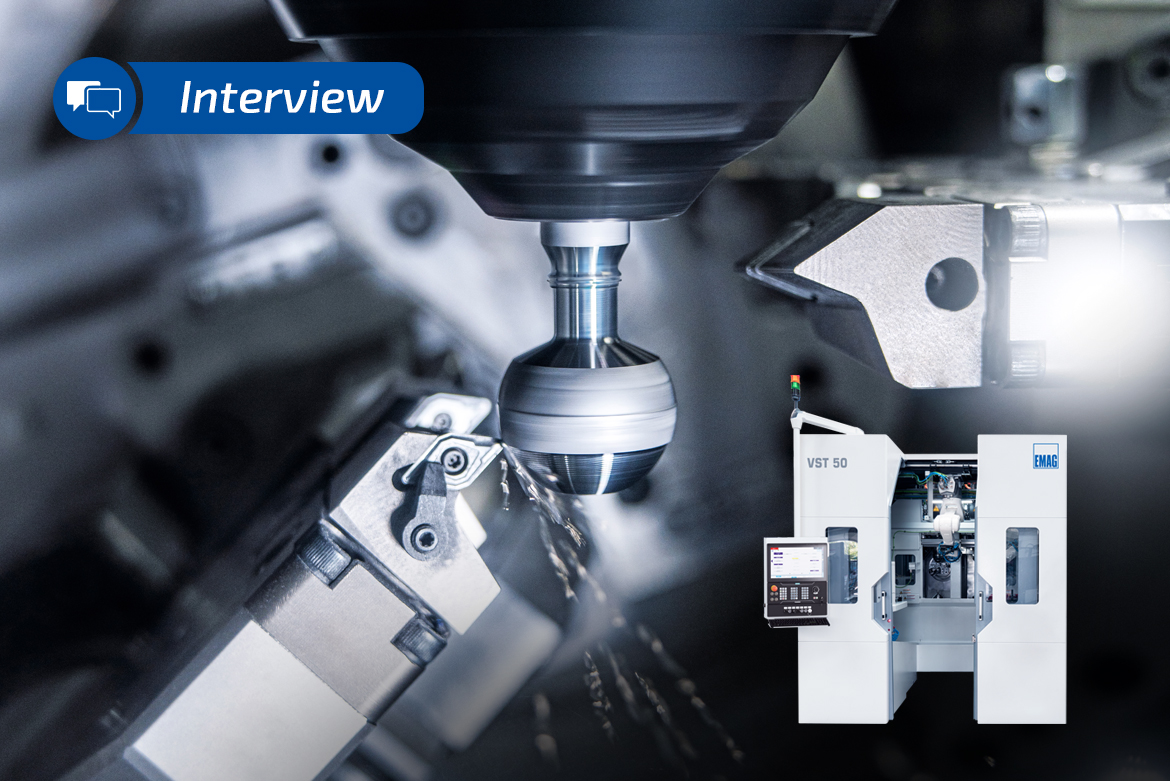
With the new VST 50 machine, EMAG is for the first time tackling a task that is as special as it is demanding: the machining of ball pins and ball sleeves. In the steering or suspension of cars, for example, these components are indispensable. What are the details of the VST 50 and how can extreme chip-to-chip times of less than two seconds be achieved in this field? Read more about this challenge in our conversation with Dr. Mathias Klein, CSO of the EMAG Group.
Vertical Turning Machine
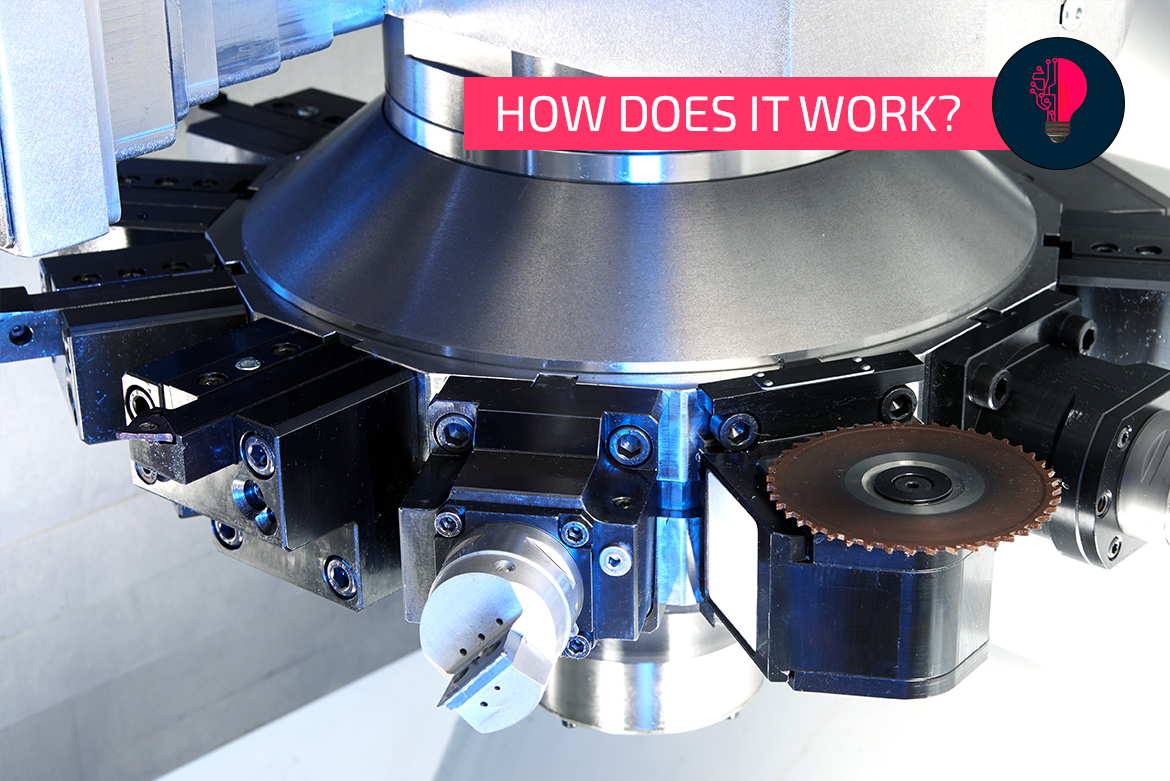
Actually, the turret inside a machine tool bears little resemblance to the barrel of a firearm in purely visual terms. So where does this name come from? We explain this in the following “How it works” blog. The same applies to the questions of how the whole thing works in detail and who invented it. Incidentally, the latter has a lot to do with the history of EMAG.
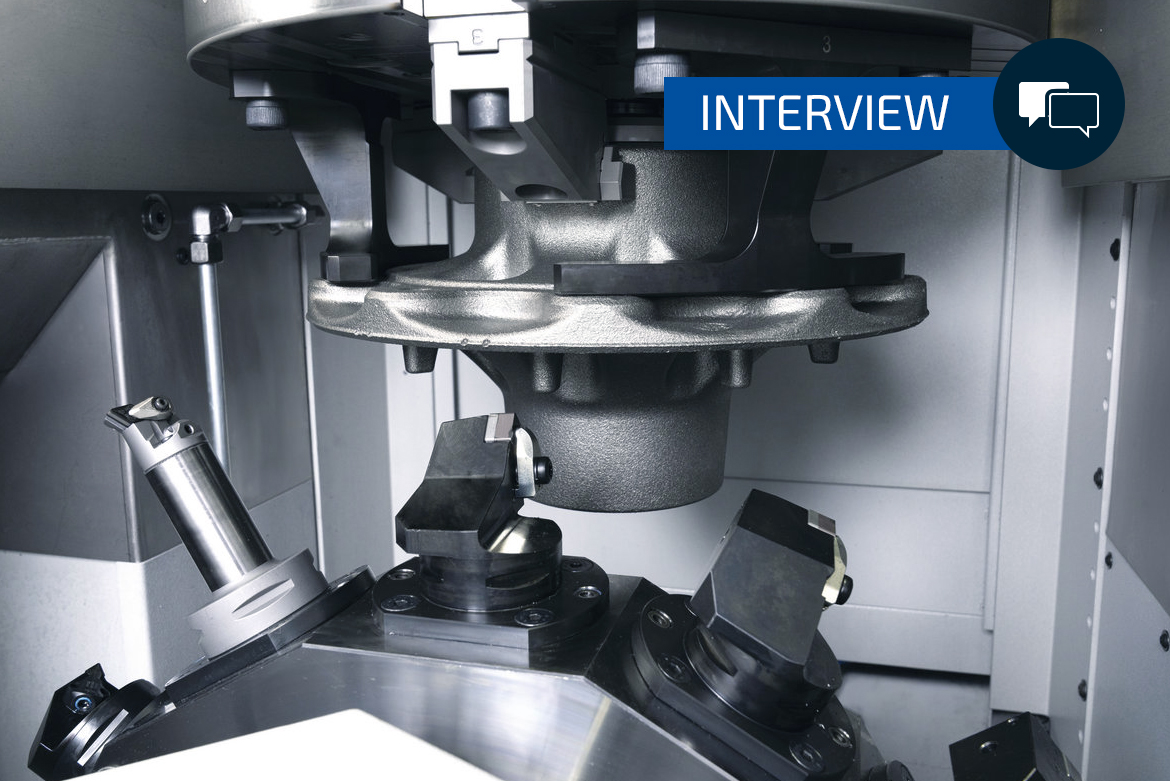
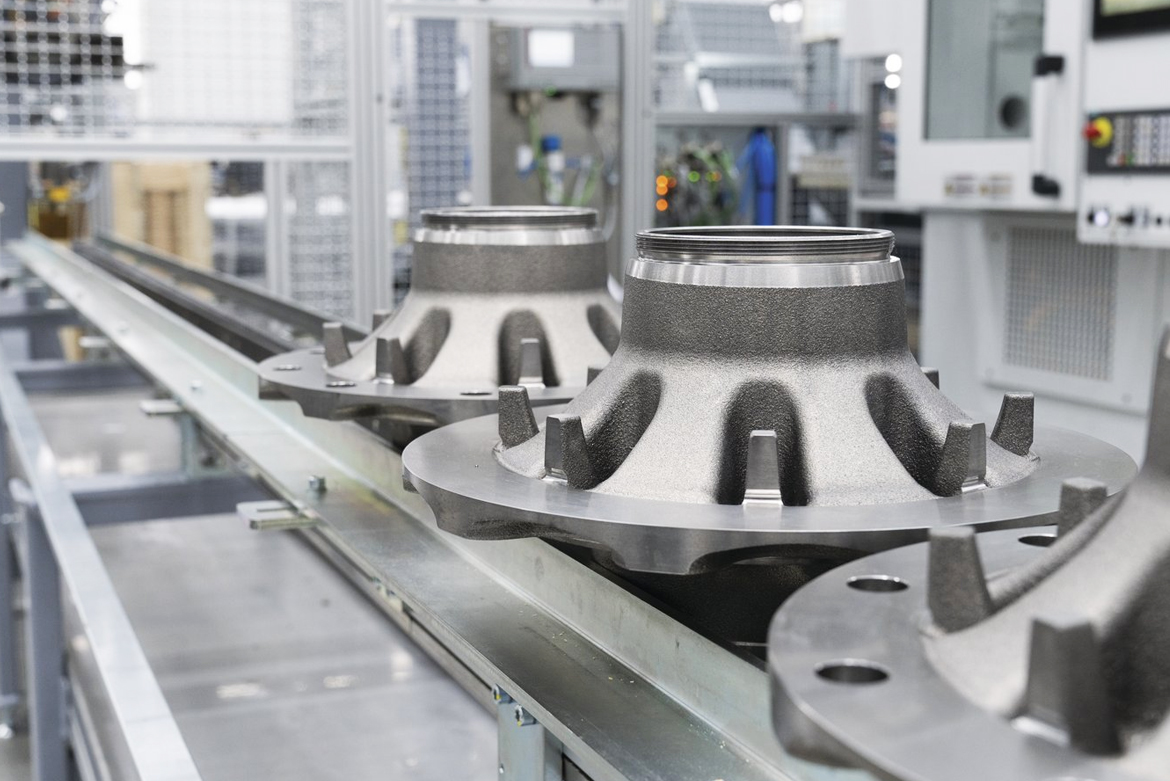
How can particularly large and heavy components be produced using lean production solutions? This question is becoming increasingly important, especially in the commercial vehicle sector, because price pressure in the market demands the lowest possible unit production costs. In this context, the VSC 500 and VSC 500 DUO machines from EMAG are real “game changers” for manufacturers. They load themselves and then ensure fast and precision complete-machining in a single setup or two. A conversation with Peter Gröner from the Turning Business Unit at EMAG about the enormous possibilities of this technology.
High precision, fast processes, small footprint – the VSC 500 and VSC 500 DUO vertical pick-up machines ensure efficiency in the machining of large components, such as those required in the commercial vehicle sector. They load themselves and then start complete-machining in a single setup or two setups (DUO).
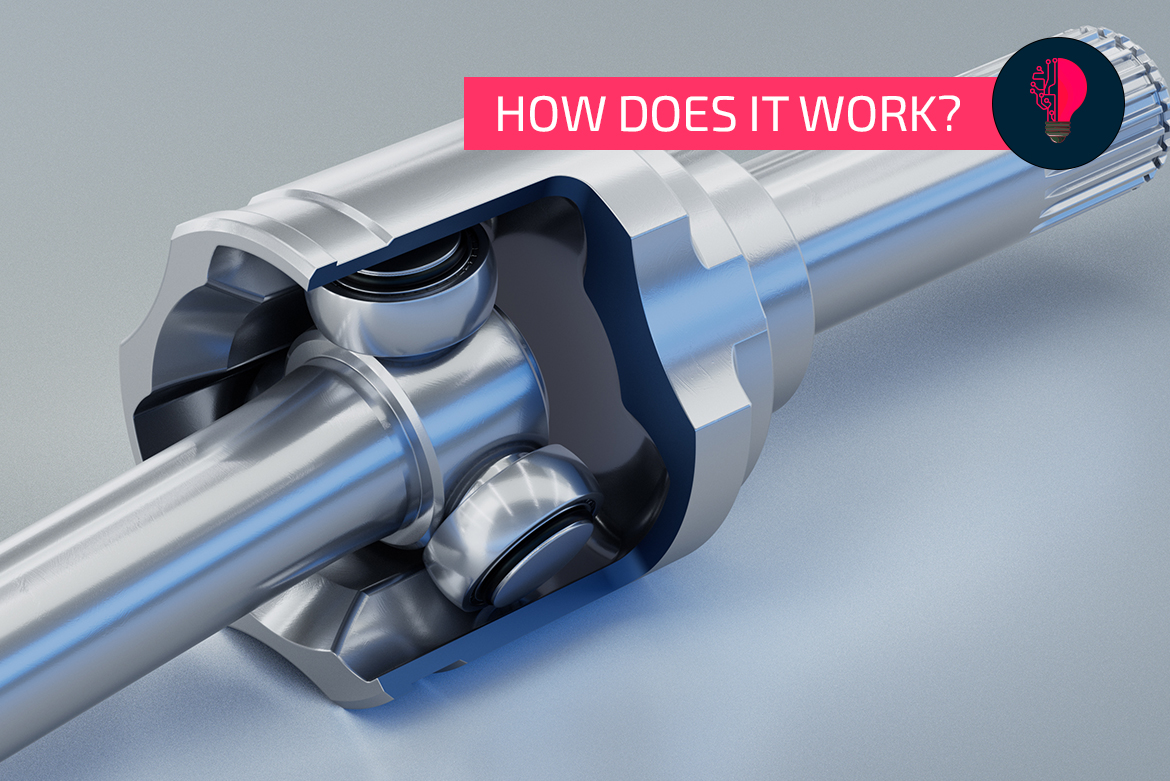
Without the tripod joint, the drive in a car would be inconceivable: The relatively small component creates the power connection between the axle drive and the drive shaft. Why is this technology so important?
The gear skiving process, also known as power skiving, is becoming increasingly popular with many users in the manufacture of gear components. This is no coincidence: compared to the shaping process, it is significantly faster and also offers more flexibility than hobbing and broaching. However, for a long time it was considered relatively complex. In this context, the VSC 400 PS represents a turning point – the application of power skiving is significantly simplified, as only minimal data is required from the operator, eliminating the need for extensive expertise in gear cutting. To take a closer look at the technology behind the VSC 400 PS and its impact on the industry, we interviewed Daniel Nille, Head of Technology Development for EMAG Power Skiving.
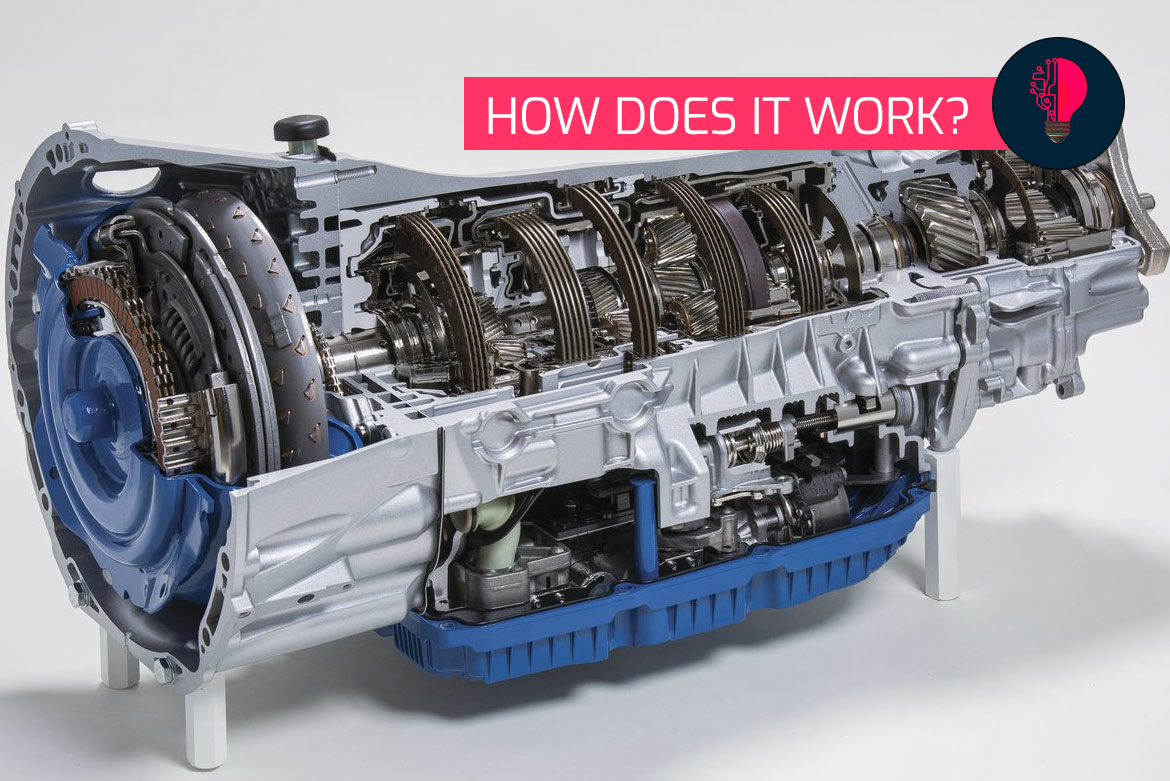
Planetary gears have been around for over 200 years – the first one was used in a steam engine at the beginning of the 19th century. The technology is still indispensable in cars, for example. What distinguishes the whole thing in detail and what are the differences in design?
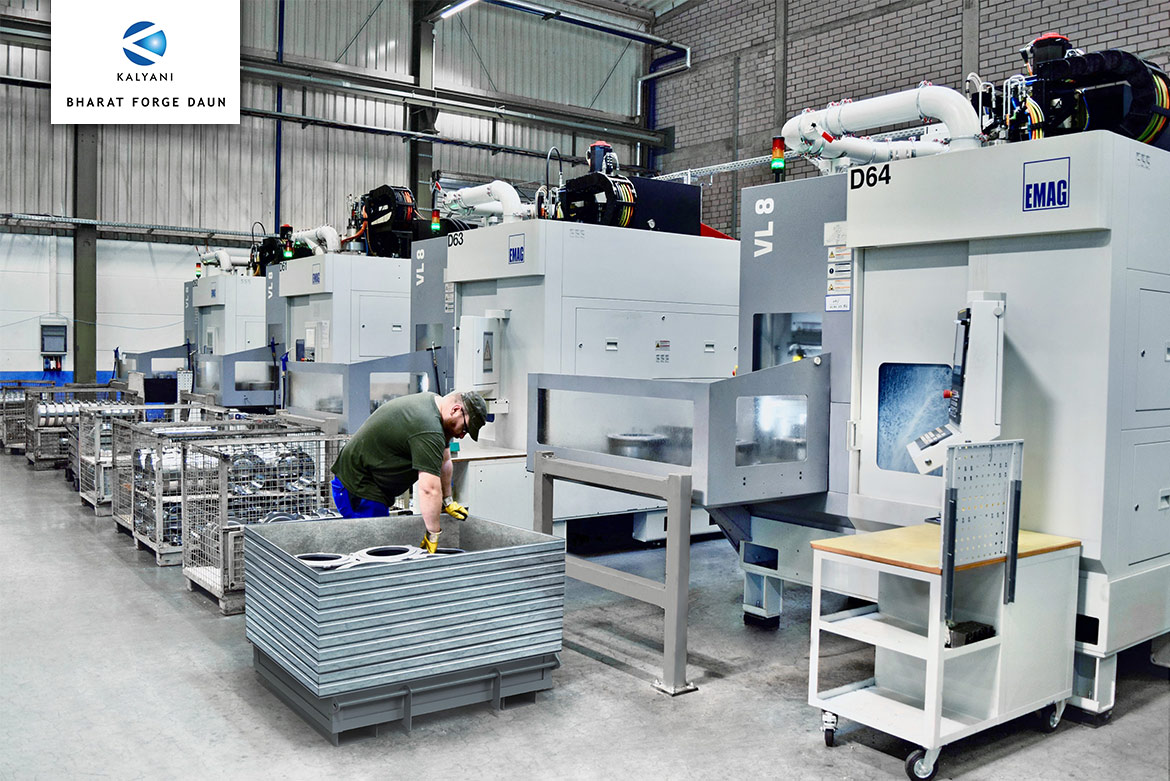
In the heart of the Eifel region, around 50 kilometers from Koblenz, Bharat Forge Daun mechanical production works at the highest level, producing extremely precise, rotationally symmetrical series components, among other things. This means that challenges like difficult surfaces and positional arrangements are common. Several EMAG machines are currently being used in the production of a stator housing for electromobility – with a focus on process reliability. In the following interview, Christoph Steffens, Head of Mechanical Production at Bharat Forge Daun, explains the reasons for using EMAG machines and why EMAG service is so important.
The integration of robot technology into manufacturing processes is playing an increasingly important role in the modern industrial landscape. Jan Gotthold, Product Manager at EMAG Maschinenfabrik, provides an exciting insight into this area. Using EMAG’s drive shaft production line as an example, he demonstrates the key benefits of this technology.
During the Open House Retrofit at the Eislingen plant, EMAG presented the future of industrial machine modernization. Visitors had the opportunity to experience the latest technologies and retrofit solutions at first hand.