In modern manufacturing , there are several processes for producing tooth profiles. Three frequently used – yet often confused – important technologies that are often confused are hobbing, skiving and power skiving. Each method has its own applications, advantages and limitations. Understanding the key differences is crucial in selecting the right technology for each job.
Manufacturing Technology
Turning balls, especially in safety-critical areas such as the automotive industry, places the highest demands on precision, repeatability and cycle time. Components such as ball pins in ball joints play a central role in steering and chassis. Their production requires state-of-the-art turning technology – especially when it comes to large quantities and economical processes.
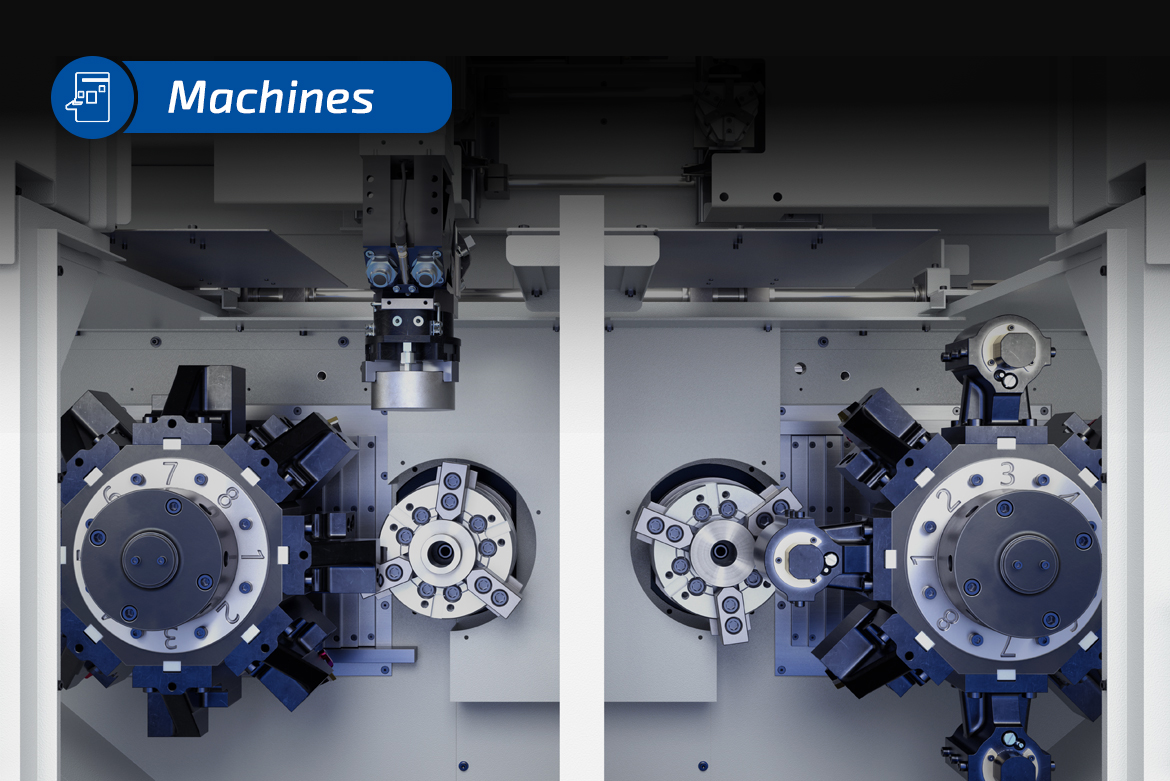
In the race to stay competitive, manufacturers are always searching for equipment that balances productivity, precision and affordability. EMAG’s Classic Machine series is designed to meet this challenge head-on. The machine front and center in this lineup, the MSC 5 DUO, exemplifies how “just enough” can be more than enough – especially when built on proven technology and smart engineering.
When the conversation turns to the topic of sustainability, most would assume green manufacturing and environmental protection will be the focus of the discussion. It’s part of the chat, Michael Tamasi, President and CEO of AccuRounds, argues, but to him and his company the term means much, much more. Yes, they’ve added solar panels to lower the plant’s carbon footprint; however, Michael knew building a company that will last involves attracting, developing and keeping talented staff. Retaining good employees also requires nurturing a creative and caring culture, and of course, operating a profitable business that provides long-term financial security as well as a good wage.